- BOOKS & MEDIA
- Books and eBooks
- Streaming media
- GUIDES & TUTORIALS
- All research guides
- Guides by subject
- Guides by special topic
- Video tutorials
Service Alert
You should use data when:
You should use statistics when:
You need quick facts to make a point or support your argument.
This quick guide from Western Libraries can help you to better understand the difference between data and statistics.
Data:
Data is made up of raw numbers, typically with many variables. These numbers often come from research that was conducted as part of a study or survey and are a primary source. Data is often in the form of a digital data set. Data is capable of being analyzed using statistical procedures. Data is used to create new information or knowledge. For example, census data provides data about the number of people within a particular area with variables such as gender, age, income, etc.
Below is an example of data:
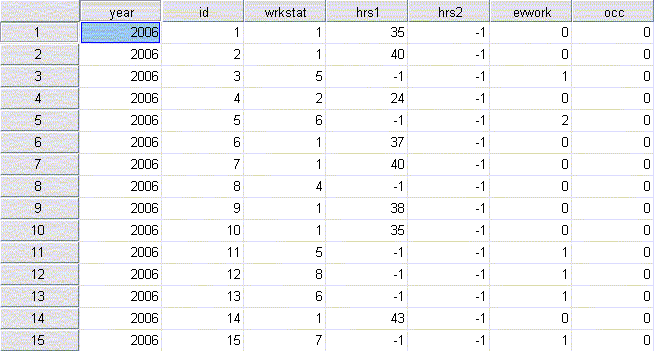
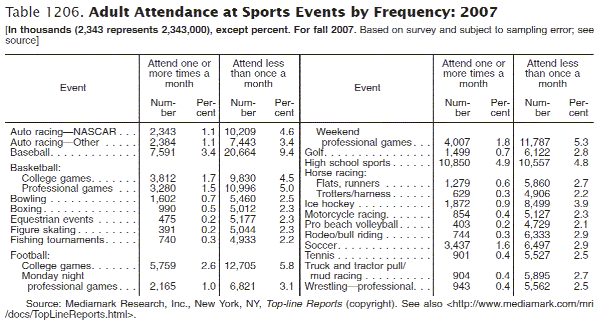
Statistics are the interpretation of raw data, often to show relationships among variables. Statistics answer “why” or “how” questions. Statistics allow you t use just a few numbers, rather than a data set, to support an argument or statement. Statistics are usually presented in tables, graphs, or charts. For example, statistics can answer such questions as to whether there is a correlation between income level and education.
Below is an example of a statistical table from Statistical Abstracts of the United States:
The following decision tree from Michigan Sate University will help guide you as you begin to seek information on your topic:

View this presentation for more information on data sets and statistics.